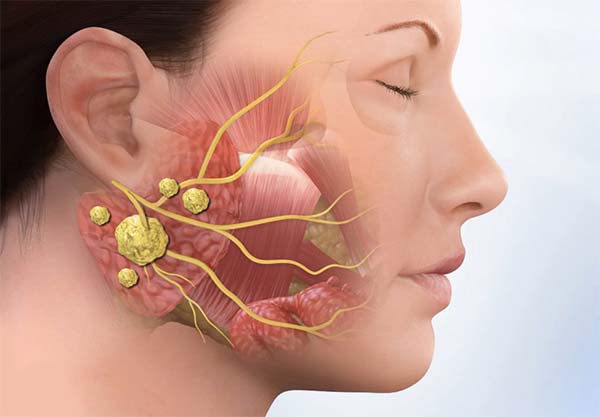
Providing surgical removal of the parotid gland tumors. The parotid gland is a salivary gland located high in the neck in the preauricular area extending towards the cheek.
The parotid gland is the largest of the glands that secrete saliva and is located just in front of the ear. The gland is divided into a deep and superficial lobe by the facial nerve which is responsible for facial movement. Tumors of the salivary glands are relatively uncommon, but when they do occur the most common location is the parotid gland. About 80 percent of these tumors are benign, the most common subtype of which is known as a pleomorphic adenoma or a benign mixed tumor. Other common benign tumors include a Warthins tumor, other types of adenomas and oncocytomas. The most common malignant tumor of the salivary gland is mucoepidermoid carcinoma which can be subdivided into tumors which are more or less aggressive. Other less common malignant tumors include adenoid cystic carcinoma, acinic cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, malignant mixed tumor, malignant oncocytoma, squamous cell carcinoma, lymphoma and melanoma. The vast majority of these tumors whether benign or malignant present as a painless mass. Much less commonly these tumors can present with pain or decreased movement of the face. Some malignant tumors can metastasize to the lymph nodes in the neck and may present with a neck mass as well.
Diagnosis of parotid tumors are usually based on physical examination and the pathology is often determined by a fine needle aspiration. This is a quick and minimally invasive biopsy which carries virtually no risk of seeding the tumor to the skin. Depending on the size and location of the tumor you may have imaging such as a CT scan or MRI to guide treatment.
Although tumors such as the pleomorphic adenoma are benign, most carry a small chance of malignant degeneration, and with time can compress the facial nerve, therefore excision is generally recommended. For benign tumors this usually means that only part of the gland will need to be removed. However for large tumors and most tumors that harbor a malignancy the entire gland will need to be removed. In malignant tumors that have grossly invaded the facial nerve, it may be necessary to sacrifice part or all of the nerve to completely remove the tumor. Most often if this is necessary the surgeon will graft the cut part of the nerve to allow for some preservation of function. Furthermore, for aggressive tumors and for those that also present with a neck mass the surgeon may also perform a dissection of some or all of the lymph nodes on that side of the neck. Occasionally, also for more aggressive neoplasms, radiation may be necessary.
Having parotid surgery is overall very safe and serious complications are uncommon. the most common problems patients have after parotid surgery can include bleeding, infection, recurrence, temporary or permanent facial paralysis, facial sweating when eating (Frey's syndrome) and a salivary fistula (remaining salivary tissue forms a cyst that may communicate with the skin). Fortunately, in expert hands the risk of these complications is low, and when they do occur surgeons possess the skills to treat them as they arise.
If you have any questions about parotid surgery please feel free to give us a call.